
MOLEAER©
Advancing Nanobubble Technology – Waste and Waste Water Treatment
Enhancing Wastewater Treatment Process Processes
 Implementing nanobubble-enabled surfactant removal in wastewater treatment is an effective and low-cost solution:
Implementing nanobubble-enabled surfactant removal in wastewater treatment is an effective and low-cost solution:
-
-
-
- Optimize plant operations and reduce O&M costs
- Increase treatment capacity
- Simple implementation
- Simple operation
- The existing plant can continue to operate while adding a Moleaer System
-
-
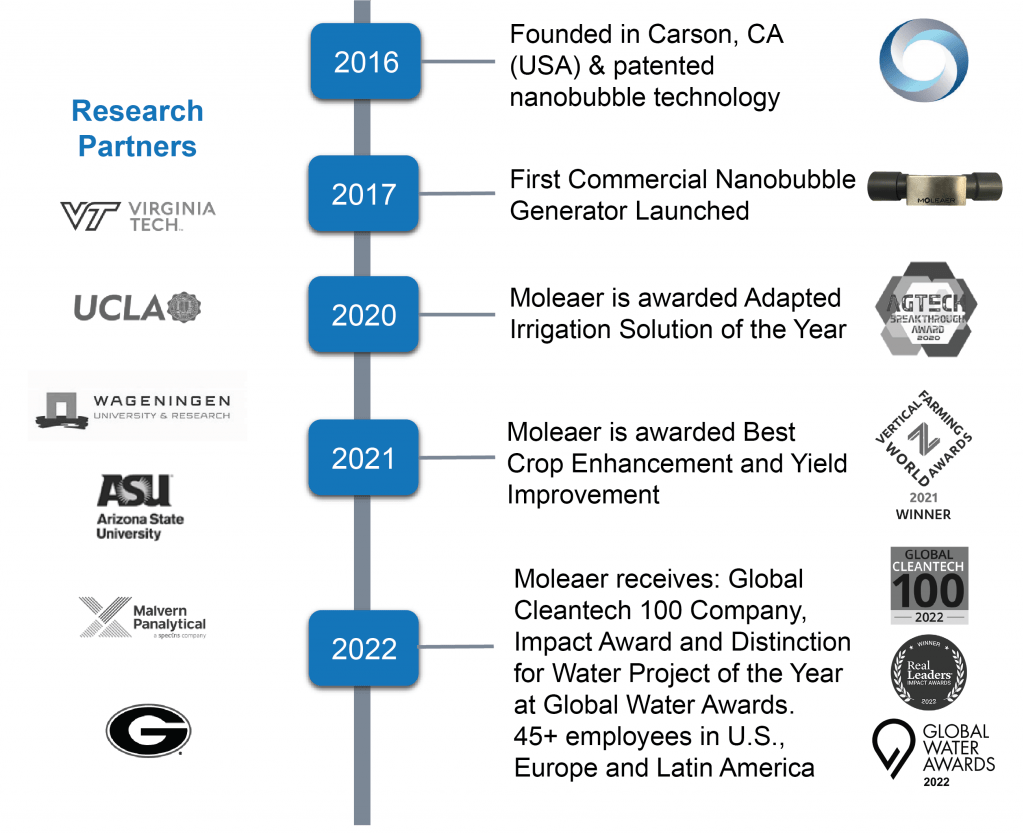
Leader in Nanobubble Technology
Moleaer™ is the global leader in manufacturing industrial-scale nanobubble systems that deliver extraordinary improvements in sustainable food production, chemical-free water treatment, and the recovery of natural resources
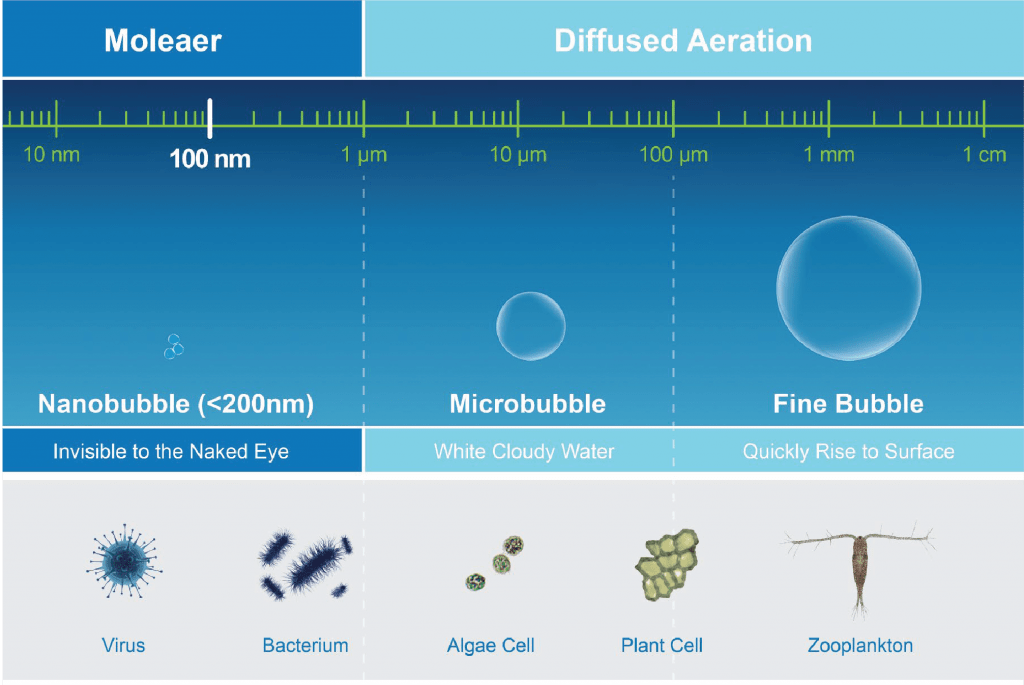
What are Nanobubbles?
A form of chemistry that increases productivity and solves climate-driven challenges, sustainably
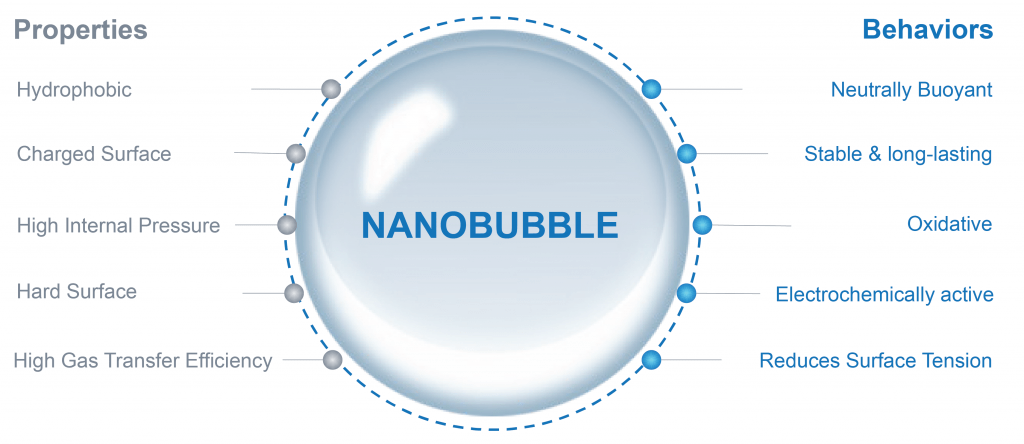
- Nanobubbles are nano-size bubbles, 2500x smaller than a grain of salt
- Lack the buoyancy to float to the surface and “pop”
- Brownian in nature and behave more like nano-sized particles
- Depending on the gas and the bubble’s charge, nanobubbles can enhance a wide range of physical, chemical and biological reactions in aqueous processes
Fundamentals of Nanobubbles
Nanobubble Benefits for Wastewater
Independent Validation
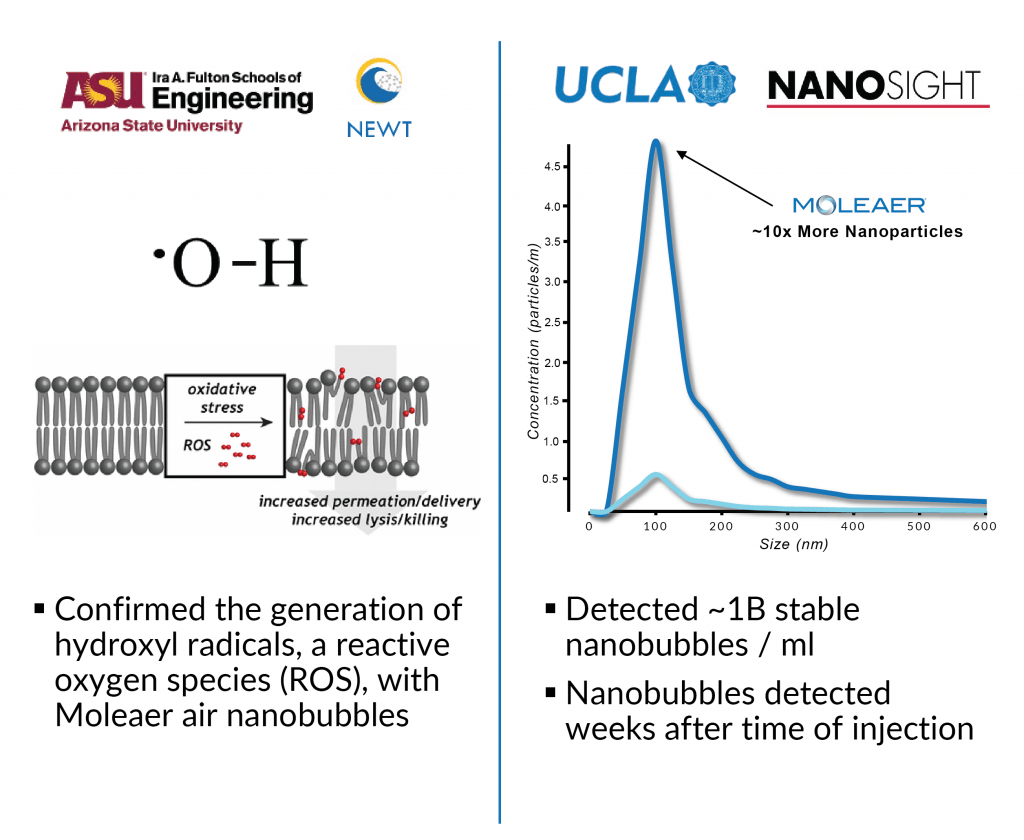
Moleaer’s nanobubble technology has been independently validated by experts in their fields
Product Overview

ASP Performance Influencers
- Temperature
- pH
- MLSS
- SRT
- Surfactants and other inhibitors
- Biological loading
- Basin depth
- Type of aeration device
- Surface aerators
- Coarse bubble diffusers
- Fine bubble diffusers

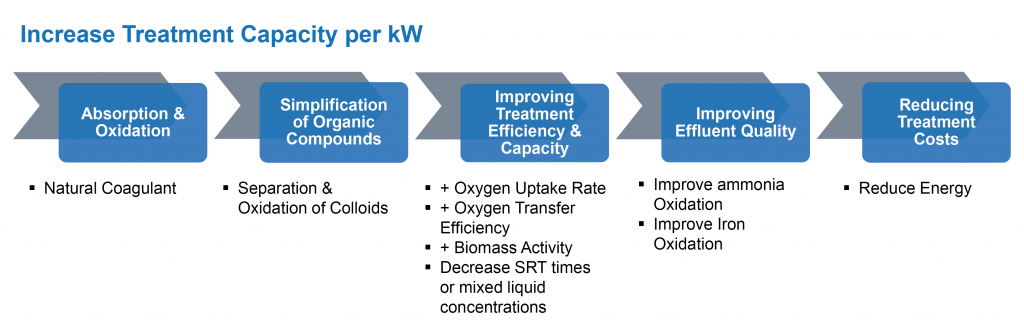
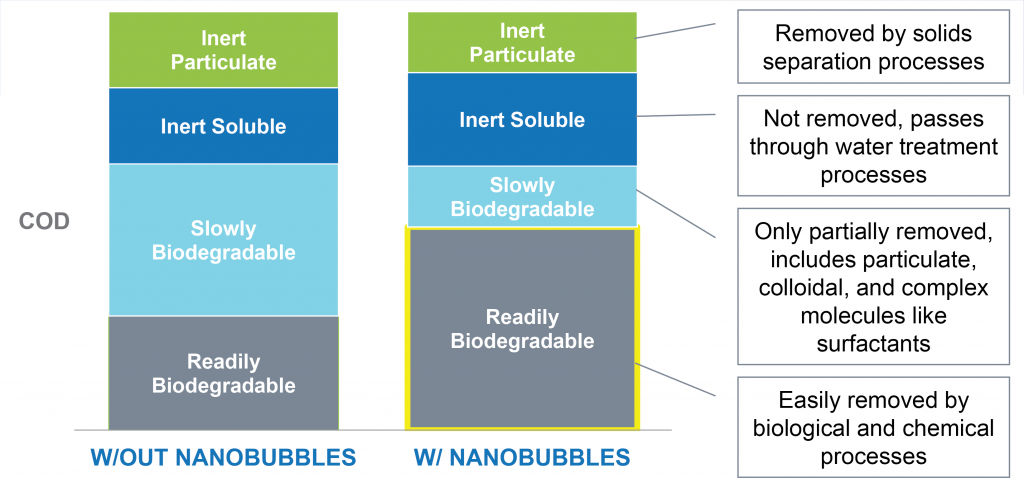
Improve Treatability & Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment
Oxygen Efficiency
- Oxygen needs to transfer into the process twice to be effective
- Oxygen needs to be diffused into the water
- Oxygen in the water then needs to be utilized by the biomass
- Any inefficiency in the transfer or utilization of oxygen costs energy
- By improving oxygen transfer and oxygen uptake rate, we can:
- Significantly improve the performance of the system
- Lower operating costs

The Problem -Surfactants
- One of the main inhibitors to the Activated Sludge Process
- Often present in both municipal and industrial waste streams
- Often categorized by ionic charge
- Quickly adsorbed by the biomass, lowering oxygen transfer to the biomass
- Inhibit oxygen transfer efficiency
- Inhibit the dewaterability of the sludge
- Continue to the effluent polluting the receiving body
- Removing surfactants is beneficial

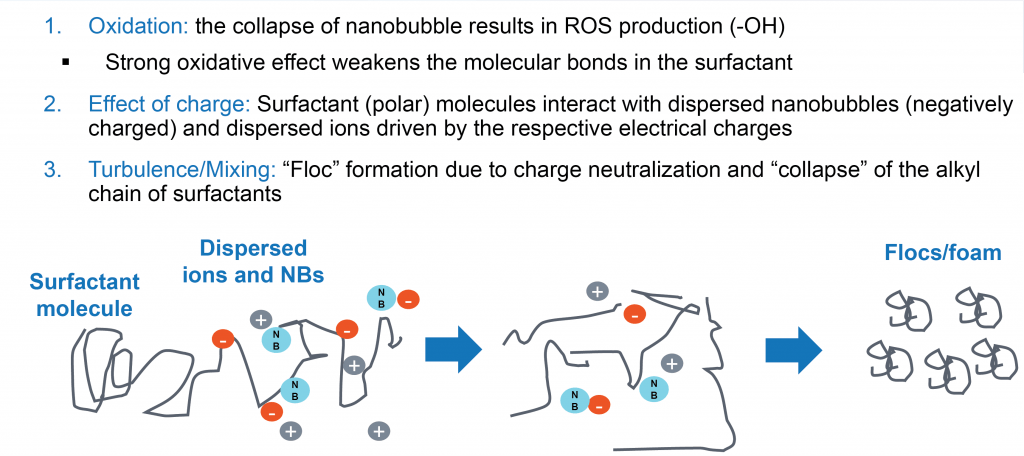
How Nanobubbles Remove Surfactants
- Oxidation: the collapse of nanobubble results in ROS production (-OH)
Strong oxidative effect weakens the molecular bonds in the surfactant - Effect of charge: Surfactant (polar) molecules interact with dispersed nanobubbles (negatively charged) and dispersed ions driven by the respective electrical charges
- Turbulence/Mixing:“Floc” formation due to charge neutralization and “collapse” of the alkyl chain of surfactants
Nanobubbles & Oxygen Transfer
- Improve EXISTING aeration systems efficiency with nanobubbles
- Klaand resultant Alpha can be raised by introducing nanobubbles
- Increases oxygen transfer efficiency of existing aeration system
- OUR can be improved further improving the system performance
- Hydrolysis can be improved allowing greater production of biogas and/or easier dewatering of sludge
- Introducing nanobubbles at the earliest stage of the process is most effective

Moleaer Solution for Wastewater Treatment
 Treatment of wastewater with nanobubbles to remove surfactantsupstream or in Activated Sludge (AS) processes to
Treatment of wastewater with nanobubbles to remove surfactantsupstream or in Activated Sludge (AS) processes to
- Reduce cost of aeration in secondary treatment (USD/MGD of influent treated)
- Increase treatment capacity in AS processes (by increasing biomass kinetics)
- Increase biogas production and energy recovery from anaerobic digestion
The injection of nanobubbles in the wastewater can be added:
- “in-line”: with a nanobubble generator (NBG) flanged into the existing piping system
- “off-line”: with a NBG configured to recirculate the wastewater in a treatment basin
